Jaundice - Atlas of swine pathology
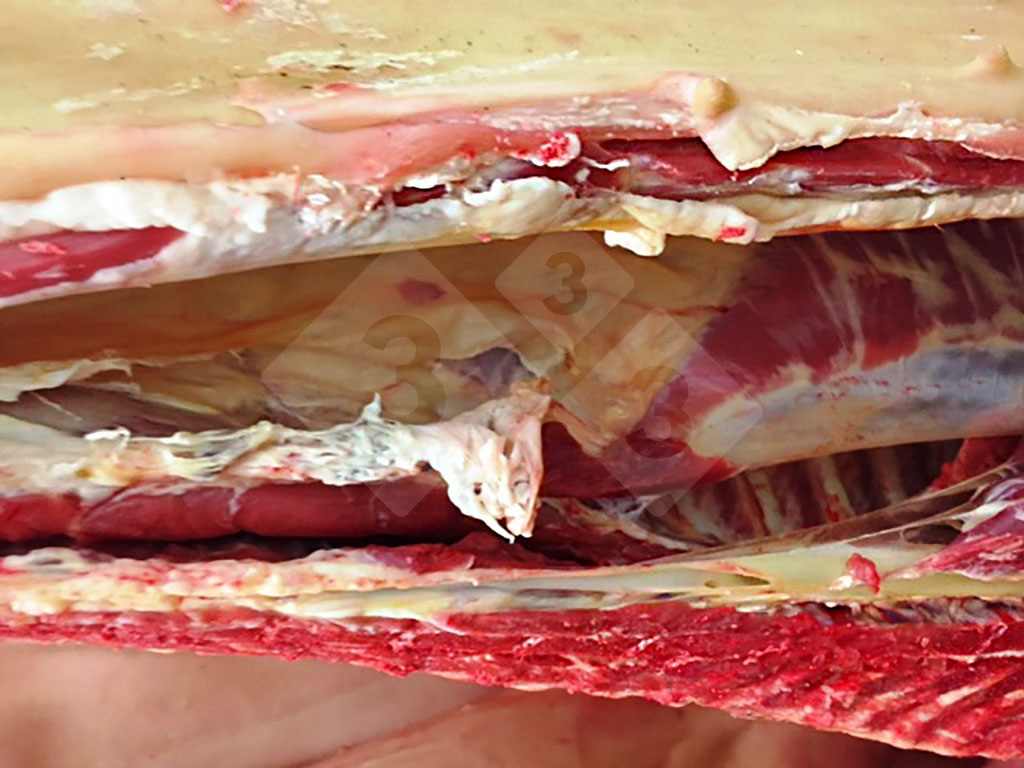
Where: musculoskeletal system
Possible causes: Mycoplasma suisLeptospirosisAscariasisAflatoxicosisFumonisin toxicosisOther
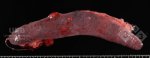
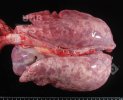
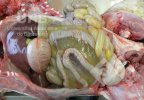
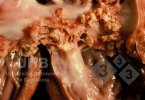
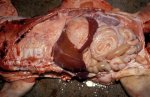
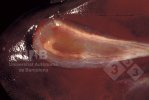
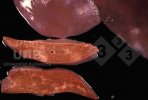
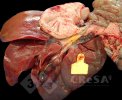
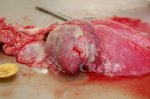
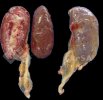
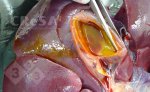
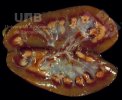
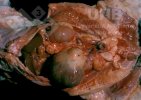
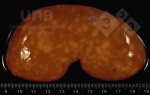
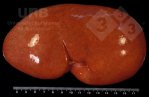
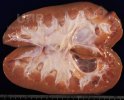
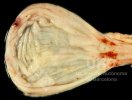
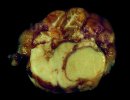
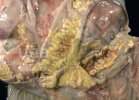
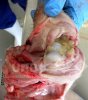
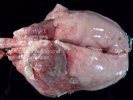
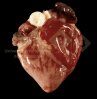
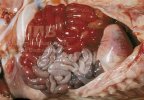
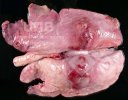
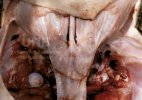
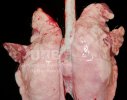
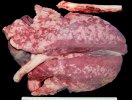
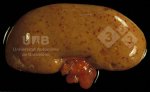
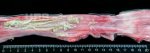
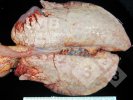
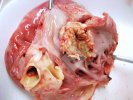
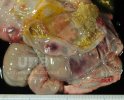
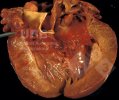
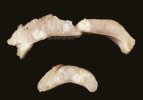
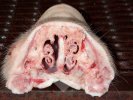
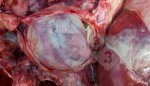
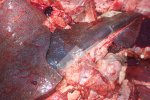
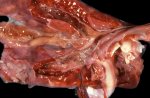
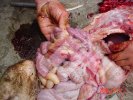
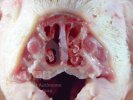
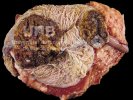
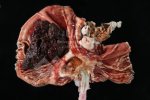
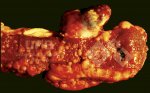
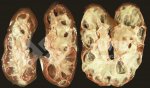
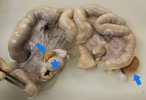
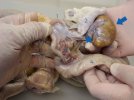
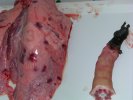
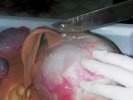
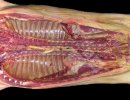
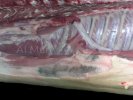
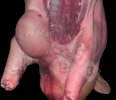
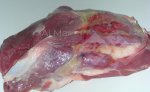
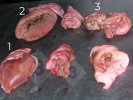
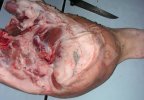
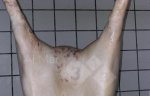
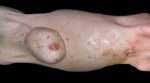
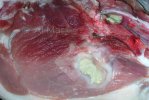
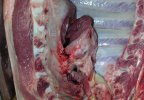
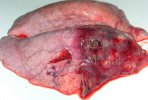
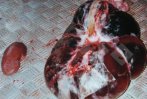
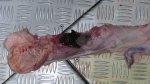
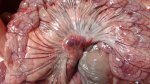
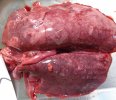
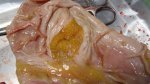
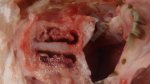
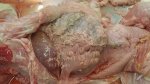
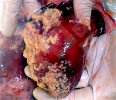
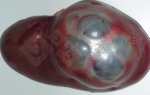
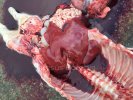
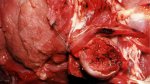
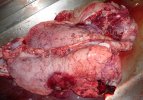
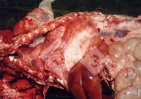
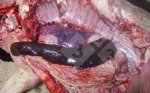
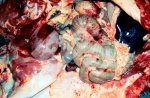
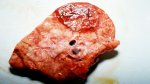
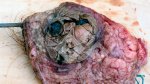
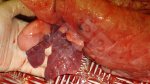
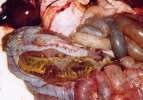
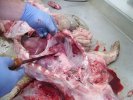
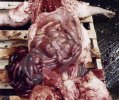
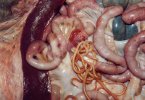
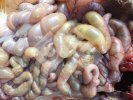
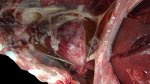
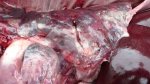
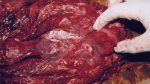
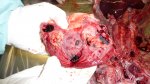
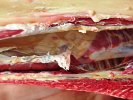
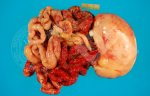
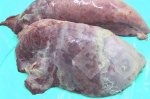
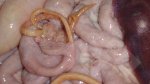
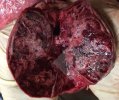
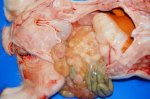
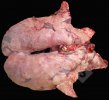
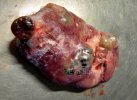
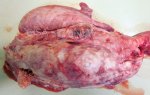
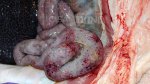
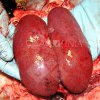
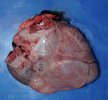
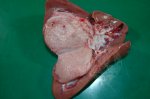
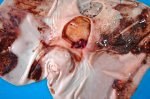
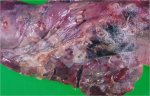
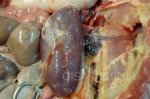
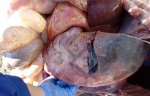
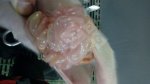
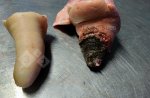
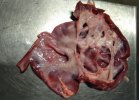
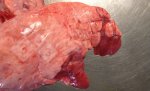
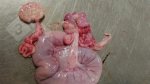
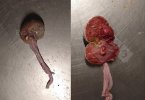
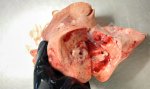
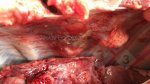
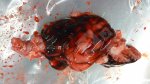
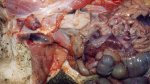
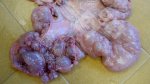
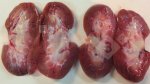
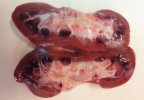
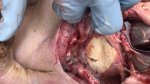
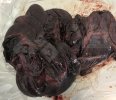
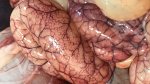
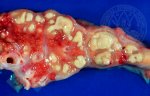
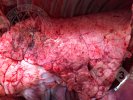
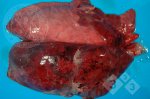
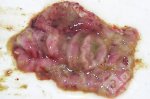
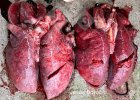
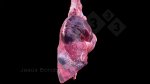
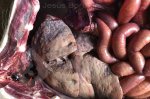
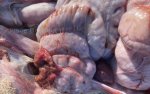
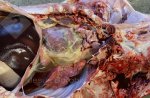
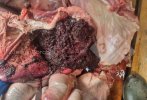
In this case, jaundice was the consequence of a heavy Ascaridiasis (Ascaris suum) infestation in the animals that caused severe milk spot lesions in the liver.
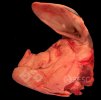
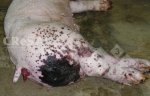
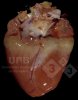
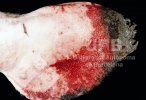
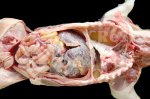
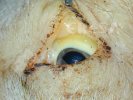
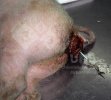
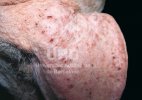
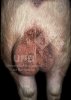
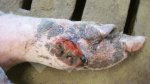
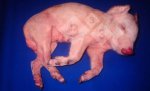
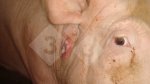
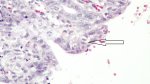
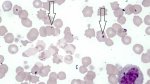
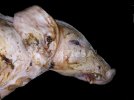
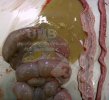
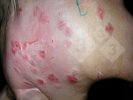
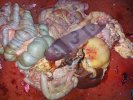
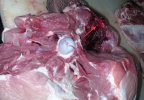
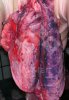
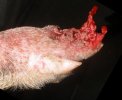
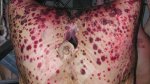
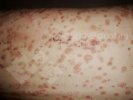
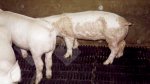
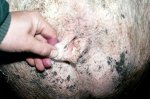
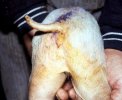
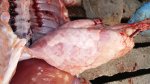
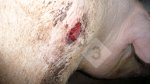
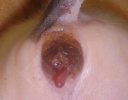
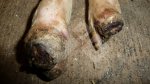
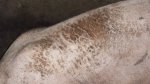
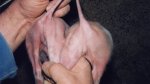
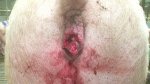
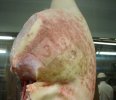
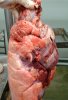
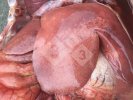
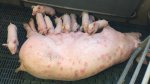
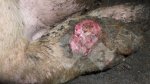
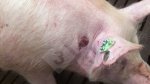
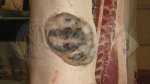
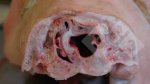
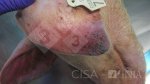
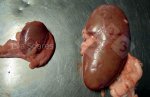
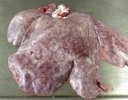
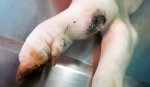
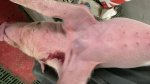
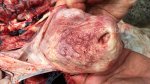
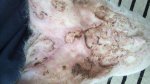
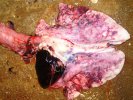
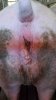
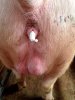
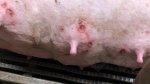
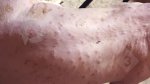
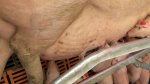
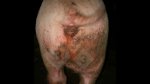
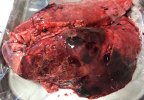
Jaundice, or icterus, is an increase of biliary salts in the blood. It is manifested as a yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes due to the breakdown of red cells in the blood, the accumulation of the bye-products in the liver and the production of a substance called bilirubin.
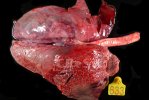
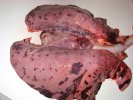
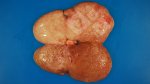
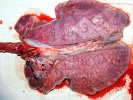
Several infections can affect directly the blood or the liver: Leptospira (mainly foetuses), Mycoplasma suis, E. coli and Salmonella. In all cases other signs can help to address infective causes. Ascaris suum can also cause jaundice through direct parasitosis of the liver which may indicate that the bile ducts are stuffed with adult ascarids. At the abattoir white spots (milk spots) are evident in the liver.
Toxicosis such as copper excess and mycotoxins (aflatoxin or fumonisin) that primarily target the liver can lead to jaundice. It can also be caused by coal tar toxicity from eating fragments of clay pigeons, builder's tar or by vitamin E and selenium deficiency.