Anaemia - Atlas of swine pathology
Where: other
Possible causes: Mycoplasma suis
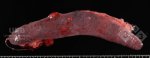
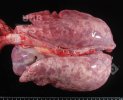
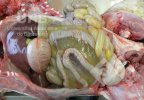
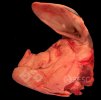
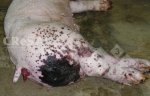
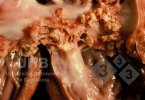
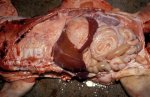
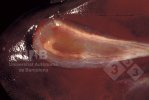
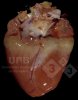
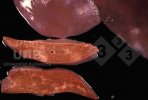
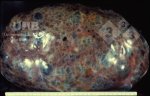
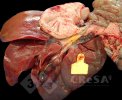
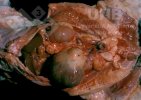
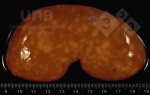
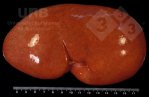
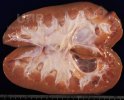
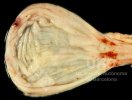
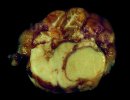
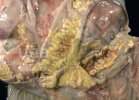
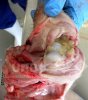
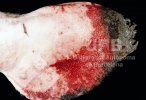
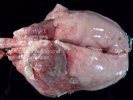
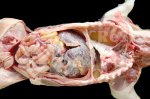
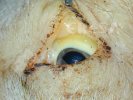
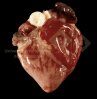
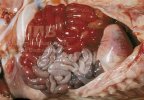
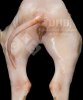
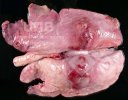
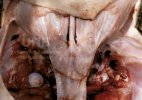
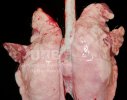
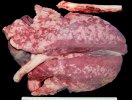
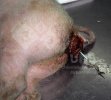
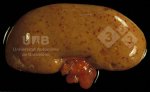
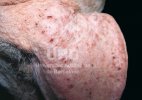
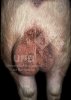
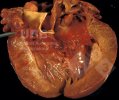
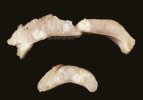
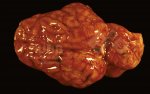
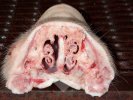
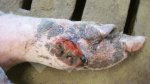
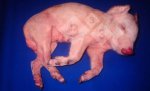
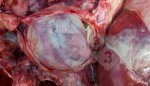
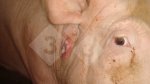
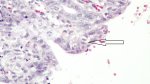
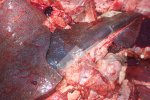
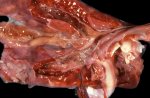
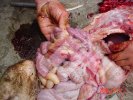
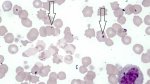
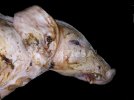
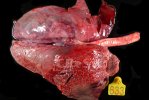
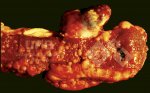
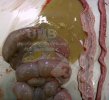
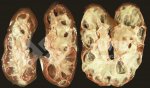
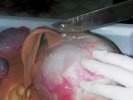
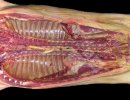
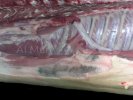
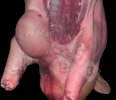
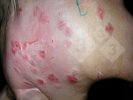
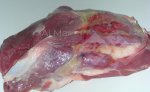
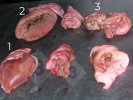
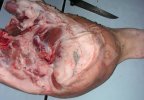
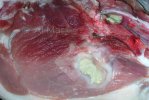
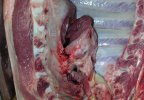
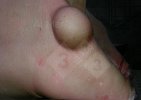
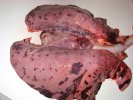
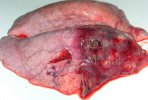
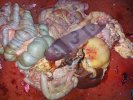
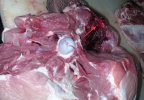
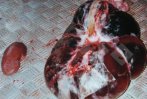
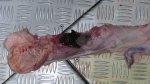
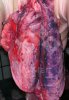
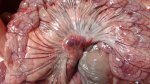
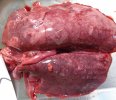
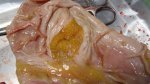
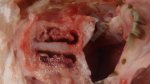
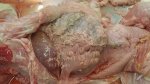
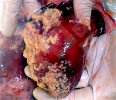
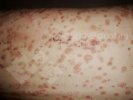
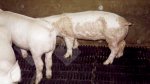
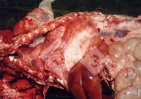
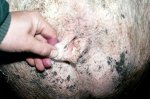
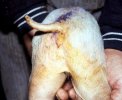
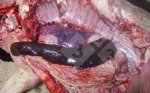
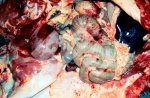
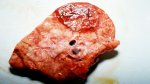
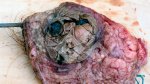
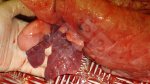
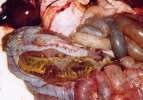
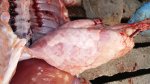
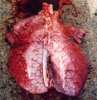
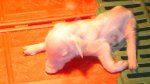
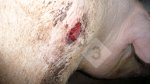
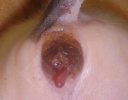
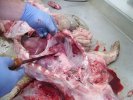
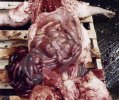
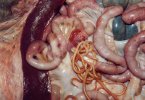
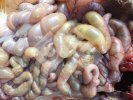
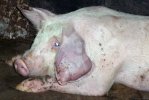
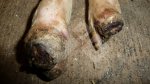
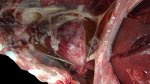
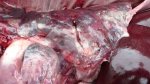
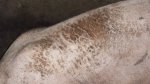
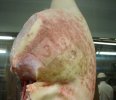
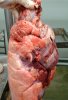
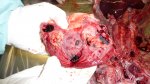
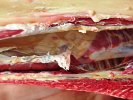
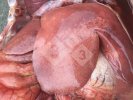
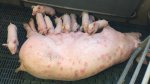
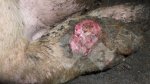
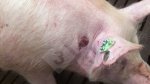
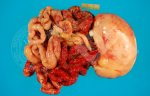
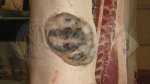
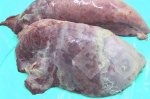
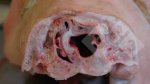
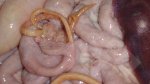
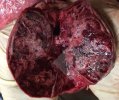
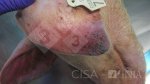
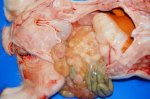
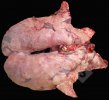
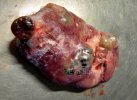
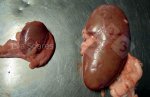
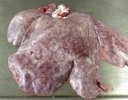
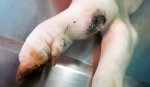
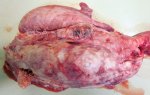
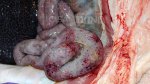
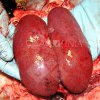
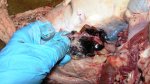
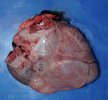
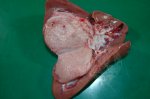
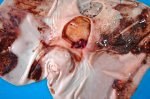
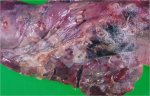
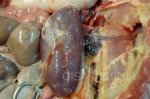
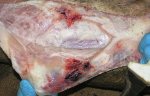
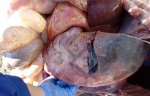
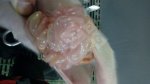
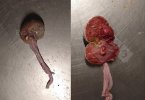
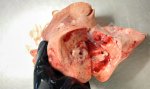
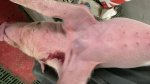
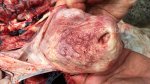
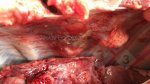
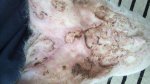
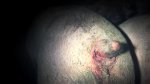
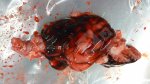
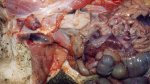
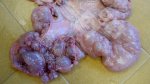
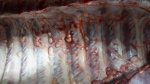
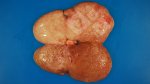
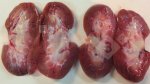
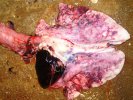
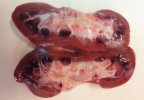
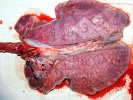
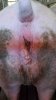
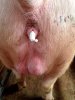
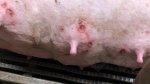
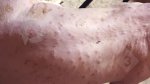
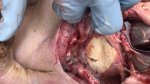
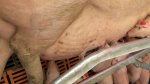
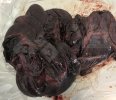
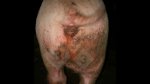
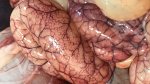
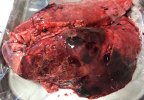
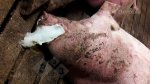
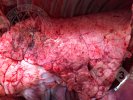
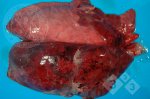
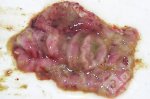
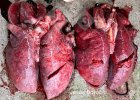
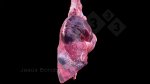
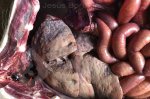
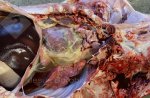
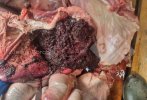
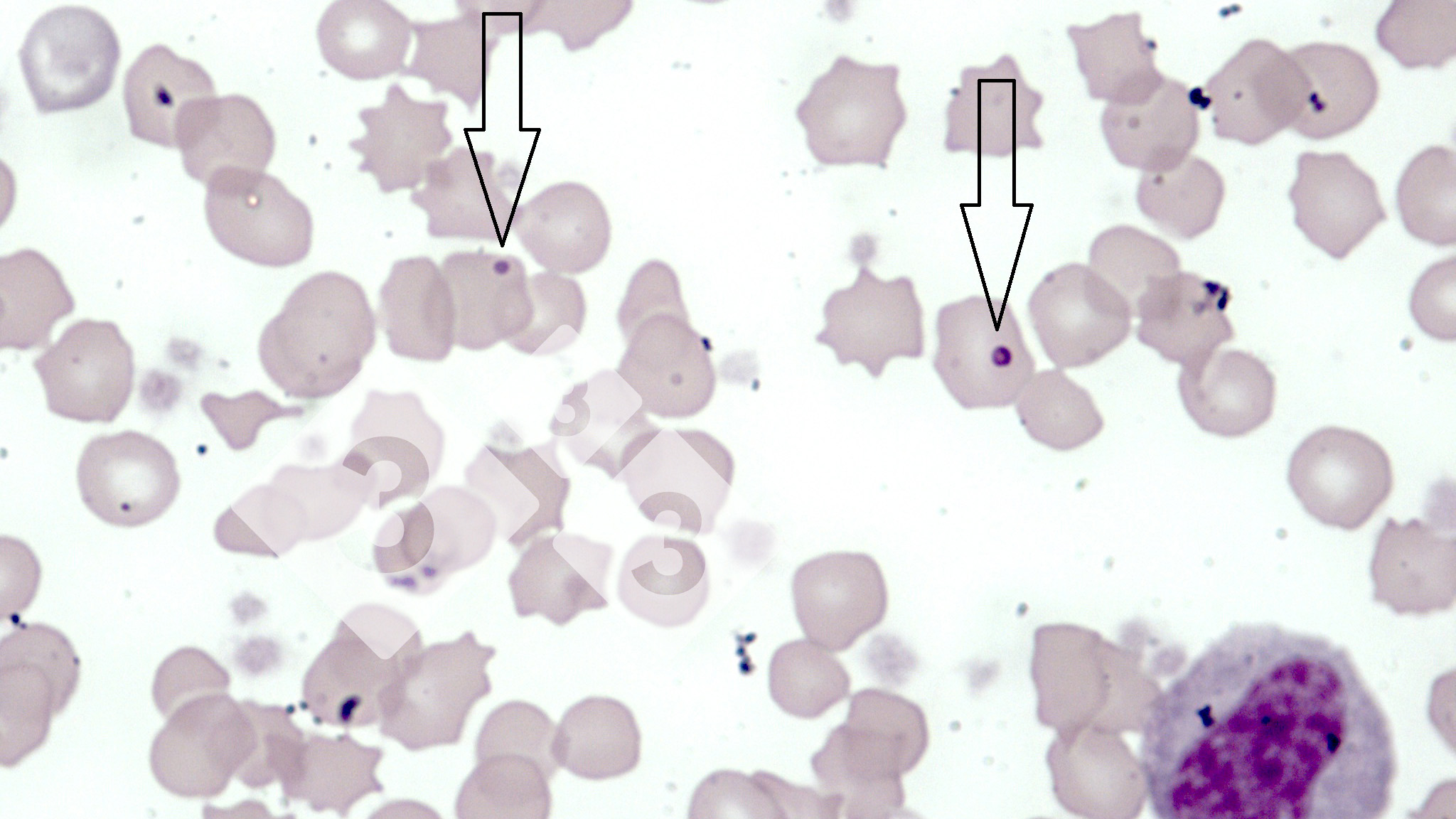
This is anaemia due to the small bacterium Mycoplasma suis (previously known as Eperythrozoon). Affected gilts appear dull, thin and pale with a low colostrum and milk yield. Anaemia in pigs may be confirmed by examination of the areas inside the sclera inside the eyelids, which are pale and white. Thin smears of blood films can be fixed in methanol and stained by routine blood stains, such as the Giemsa stain to search for the small Mycoplasma suis. Typically in Mycoplasma suis infections, the red cell counts are very low, such as 4.2 to 5.5 x 106 cells per mm3 of blood, compared to a suggested normal range of 5.6 to 9.5 x 106 cells per mm3. This disease occurs sporadically in groups of pigs, where needles and syringes and farm equipment are shared among different pigs. This may act to spread the infection from one infected group of pigs to another, such as from old to new breeding pigs.