Assays available
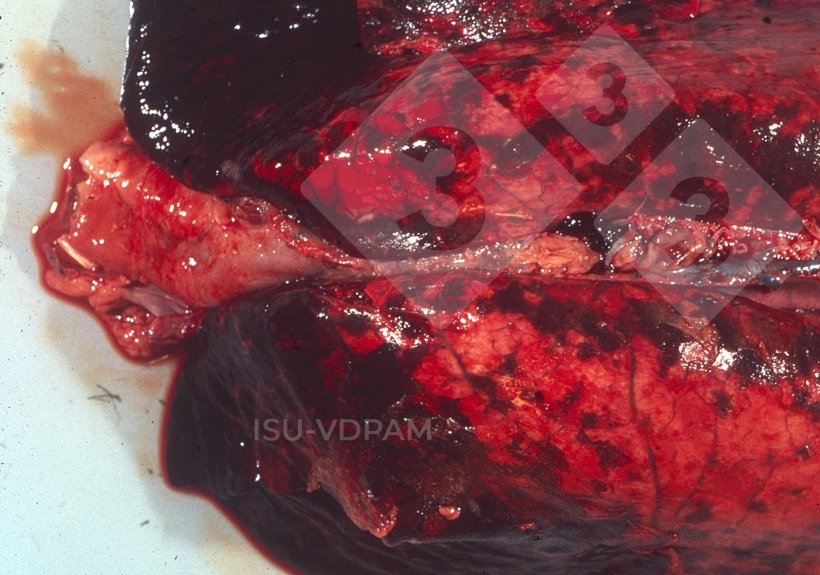
Gross pathology
- Evaluates the presence of tissue lesions which can almost be diagnostic for the disease.
- Location of lesions: lung
- Necro-hemorrhagic areas of consolidation in the lung accompanied by fibrinous pleuritis (see Figure 1).

- Pros:
- Presumptive diagnosis can be made after gross examination of lungs.
- Cons:
- Actinobacillus suis can cause some similar lesions although less severe.
- Cannot identify serotype.
Bacterial culture
- Isolation of live organism
- Sample types: lung
- Pros:
- Can do in any lab (including in-house)
- Biotype I requires NAD (usually provided via Staphylococcus aureus nurse colony)
- Biotype II does not require NAD
- Relative low cost
- Cons:
- Not always easy to grow
- Cannot serotype
- Pigs previously treated with antibiotics can prevent bacterial growth
Antimicrobial susceptibility
- Tests in vitro ability of live organism to grow under specific concentrations of different antimicrobials
- Sample types: lung
- Pros:
- Identification of susceptibility or resistance of specific isolate to common antimicrobials
- Identification of antimicrobial resistance trends
- Cons:
- Requires a bacterial isolate
- In vitro testing may be slightly different than in vivo results
- Some specific antimicrobials may not be tested or require separate, special testing
- Moderate cost
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) General or Serotyping
- Detects presence of specific sequence of bacterial nucleic acid (DNA)
- Sample types: lung and tonsil
- Pros:
- High sensitivity
- General
- Target ApxIV toxin genes
- Present in all APP serotypes
- Serotyping
- Target different parts of ApxI, ApxII, and ApxIII toxin genes
- See Table 1 for serotyping and toxin production
- Moderate cost
- Can often do pooling of tissue samples to lower cost while minimizing loss of sensitivity.
- Cons:
- Require several specific PCR primers to determine serotyping
- Not all isolates are typable
- Currently 19 serotypes identified and growing
- Not all assays validated for testing tonsil tissue
Table 1: Toxin production for each serotype.
| Toxin Production | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serotype | ApxI | ApxII | ApxIII | ApxIV |
| 1 | X | X | X | |
| 2 | X | X | X | |
| 3 | X | X | X | |
| 4 | X | X | X | |
| 5 | X | X | X | |
| 6 | X | X | X | |
| 7 | X | X | ||
| 8 | X | X | X | |
| 9 | X | X | X | |
| 10 | X | X | ||
| 11 | X | X | X | |
| 12 | X | X | ||
| 13 | X | X | ||
| 14 | X | X | ||
| 15 | X | X | X | |
| 16 | X | X | X | |
| 17 | X | X | ||
| 18 | X | X | ||
| 19 | X | X | ||
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) LPS-O-Antigen
- Detects presence of antibodies
- Sample types: serum
- Target: LPS-O-Antigen
- Pros:
- Can be useful in helping serotyping
- High sensitivity
- Cons:
- Large amount of cross reactivity between serotypes due to share capsular and LPS-O antigen epitopes
- The following serotypes cross react due to shared LPS-O antigens:
- Cross reaction between serotypes 1, 9, and 11
- Cross reaction between serotypes 3, 6, 8, 15, 17, and 19
- Cross reaction between serotypes 4, 7, and 18
- The following serotypes cross react due to shared LPS-O antigens:
- Unable to determine specific serotype with just one assay
- Very expensive and impractical to test for all serotypes
- Large amount of cross reactivity between serotypes due to share capsular and LPS-O antigen epitopes
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) ApxIV antigen
- Detects presence of antibodies
- Sample types: serum
- Target: ApxIV Antigen
- Pros:
- High sensitivity
- Detects all APP serotypes
- Cons:
- Unable to determine specific serotype
- Unable to determine virulence of isolate
Result interpretation
Gross pathology
- Positive: Often presumptive diagnosis is sufficient
- Negative: No gross lung lesions
Bacterial culture
- Positive:
- Biotype 1: NAD dependent
- Biotype 2: NAD independent
- Negative: Negative or animal possibly previously treated with antibiotics
Antimicrobial susceptibility
- Susceptible: possible good choice for treatment if antimicrobial can reach target tissue
- Resistant: select different antimicrobial
- MIC: are done to ensure the antimicrobial selected achieves the listed MIC value in the target organ
PCR
- Positive:
- Organism present
- Can identify presence of different genes which can help serotype
- Negative:
- Negative or too late after infection.
- Animal possibly previously treated with antibiotics
- Not all isolates can be serotyped (Non-typable)
ELISA LPS-O-Antigen
- Positive: help serotype or identify group of serotypes
- Negative: negative, too late after infection, or animal possibly previously treated with antibiotics
ELISA ApxIV antigen
- Positive: Organism present
- Negative: negative, too late after infection, or animal possibly previously treated with antibiotics
Scenarios
Growing pigs with sudden death or respiratory disease (acute)
- Necropsy of 1-3 recently dead or euthanize coughing pigs. Grossly evaluating lung for necro-hemorrhagic areas of consolidation accompanied by fibrinous pleuritis.
- Submit affected lungs for bacterial culture and APP PCR general testing and if positive then for PCR serotyping.
Establish negative status of herd
- Sample 30 of largest finishing pigs on farm and test 2-3 times a year using ApxIV ELISA.




