Maximum tension at the seams (and the heart) of the market
The pig price in Spain is well above the rest of the European countries. The reality is that this price is only possible at the expense of negative margins in the slaughterhouses.
The pig sector events all around the world
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Swine industry news in your email
Pig health: news and articles on PRRS, PCV2, biosecurity, etc, Pig disease guide, atlas of pathology, clinical cases…
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
A visual and practical step-by-step guide on how to perform a necropsy on a pig.
All the information about ASF: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, pictures of lesions, latest news, guides, etc.
All the information on Foot and Mouth Disease in pigs: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, images of lesions, latest news, guides,...
Description of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs
Images of major swine diseases
Pig disease diagnostic tool
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Pig Prices by countries. Pork production and trade. News of the pig market and the raw materials
The latest slaughter pig prices in the most important pig markets. Check the evolution of the historical prices in charts and in several currencies.
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Figures & trends in pig numbers, pork production and pork trade.
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Articles on nutrition and pig feeding, characteristics of raw materials and additives for pig feed. Prices of raw materials
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Technical sheets of the main raw materials and additives used in swine feed. They include a comparison of nutritional values from various sources, product
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to diagnose problems with the feed conversion ratio. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
A biweekly newsletter with the latest developments in swine nutrition
Articles on genetics and pig reproduction: genetic improvement, genomics, artificial insemination, use of hormones
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to find out why your farrowing rate is less than ideal. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons found within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Management, pig farm management, work planning in each production stage: management in gestation, grow finish, batch farrowing
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Design of facilities and equipment for pig farms: building design, climate control, feeding systems, etc.
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
Environmental Footprint Calculator along the pork value chain.
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Use this tool to explore which slurry management strategy best fits your situation. Click on the flow chart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
List of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs. Symptoms, causes, diagnosis, control and prevention of each disease are described. Some of the treatments mentioned may be prohibited in some countries. Information on all diseases to be completed in the coming days.
Foot-and-mouth disease is one of the most important vesicular diseases.
There are four swine vesicular diseases that are not clinically differentiated: foot and mouth disease, vesicular disease, vesicular exanthema, and vesicular stomatitis.
Foot and mouth disease (FMD) is considered to be the most contagious livestock disease and the most significant restriction factor regarding international trade of animals and animal products. Essentially, all cloven-hoofed species are susceptible.
Foot-and-mouth disease belongs to the Picornaviridae virus family of which there are more than 60 strains classified into seven serotypes.
All ages
Serological and PCR tests are needed. Foot-and-mouth disease does not differentiate clinically from the rest of the vesicular diseases. Laboratory samples must include blood, vesicular tissue and fluid, when possible.
There is no treatment. There are some effective vaccines for specific serotypes.
It should be noted that there is no cross-protection between serotypes.
Foot and mouth disease affects all cloven-hoofed animals, both domestic and wild, and thus affects different species of bovines, ovines, goats, and suids. This large group includes pigs and wild boars, cattle, sheep and mouflons, goats, gazelles, antelopes, buffalo, and bison. Camelids (camels, dromedaries, llamas, and vicunas) are less susceptible to contracting the disease.
The incubation period for foot and mouth disease is 2 to 14 days, the most common being 2 to 5 days. In small ruminants (sheep and goats), the maximum period may be 21 days.
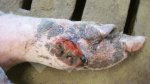
The main symptoms are: Fever, loss of appetite, prostration, lameness, ptyalism and sialorrhea (excessive salivation and difficulty keeping saliva in the mouth) agalactia, abortions; more evident in pigs and cattle and less evident in small ruminants.
The most characteristic lesions are vesicles on the tongue, gums, buccal mucosa, hard and soft palate, lips, nostrils, snout, coronary ridge, teats, udders, and interdigital space.
For more information: https://www.pig333.com/pig-diseases/foot-and-mouth-disease_43

The pig price in Spain is well above the rest of the European countries. The reality is that this price is only possible at the expense of negative margins in the slaughterhouses.

The appearance of a case of foot and mouth disease aggravated the fall in the German pig price with direct repercussions on prices in neighboring countries.

What laboratory diagnostic methods can I use to diagnose FMD? Which one should I choose according to the situation? How do I interpret the results?

You've probably heard that one of the ways the ASF virus can enter a country is through contaminated food. Here's why it's so risky.

Pathogens that are transmitted mostly through direct, pig to pig, contact are generally contained with today’s biosecurity programs and pig flow strategies. However, pathogens using multiple routes of transmission seem to evade standard biosecurity programs.

On the finisher sites, the farmer noticed that the growing pigs in all the farm sheds had become dull and lame.
World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) (2026) – WAHIS periodical extraction of early warning outbreak data. Retrieved on 2/16/2026. Data extracted by 333 Corporate 1998, SL. WOAH bears no responsibility for the integrity or accuracy of the data contained herein, not limited to: any deletion, manipulation, or reformatting of data that may have occurred beyond its control.
OTHER SOURCES
![]() What you need to know about Foot and Mouth Disease. FAO
What you need to know about Foot and Mouth Disease. FAO
Video explaining the main transmission routes and clinical signs of the disease.
![]() Foot and Mouth Disease Pocket Guide. USDA-APHIS
Foot and Mouth Disease Pocket Guide. USDA-APHIS
More than 60 pictures with lesions caused by foot and mouth disease virus after an experimental infection, both in domestic and wild pigs.
![]() Foot and Mouth Disease Technical Disease Card. World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)
Foot and Mouth Disease Technical Disease Card. World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)
Updated information from WOAH about the disease.