Laboratory diagnostics: Influenza A virus (IAV)
What laboratory diagnostic methods can I use to diagnose influenza A? Which one should I choose according to the situation? How do I interpret the results?
The pig sector events all around the world
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Swine industry news in your email
Pig health: news and articles on PRRS, PCV2, biosecurity, etc, Pig disease guide, atlas of pathology, clinical cases…
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
A visual and practical step-by-step guide on how to perform a necropsy on a pig.
All the information about ASF: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, pictures of lesions, latest news, guides, etc.
All the information on Foot and Mouth Disease in pigs: how to recognize the disease, how it is transmitted, images of lesions, latest news, guides,...
Description of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs
Images of major swine diseases
Pig disease diagnostic tool
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Pig Prices by countries. Pork production and trade. News of the pig market and the raw materials
The latest slaughter pig prices in the most important pig markets. Check the evolution of the historical prices in charts and in several currencies.
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Figures & trends in pig numbers, pork production and pork trade.
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Articles on nutrition and pig feeding, characteristics of raw materials and additives for pig feed. Prices of raw materials
Latest quotations for the main commodities used in pig feed. Historical graphs with the pig price and estimated feed price.
Technical sheets of the main raw materials and additives used in swine feed. They include a comparison of nutritional values from various sources, product
Global production and trade data for the most important raw materials
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to diagnose problems with the feed conversion ratio. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
A biweekly newsletter with the latest developments in swine nutrition
Articles on genetics and pig reproduction: genetic improvement, genomics, artificial insemination, use of hormones
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Use this tool to find out why your farrowing rate is less than ideal. Click on the flowchart or on the buttons found within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Management, pig farm management, work planning in each production stage: management in gestation, grow finish, batch farrowing
Compare production data, calculate the number of sow, nursery, and finishing spaces, and visualize your tasks on the work schedule by type of BMS.
Tool that allows you to calculate the replacement rate in your farm
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
Design of facilities and equipment for pig farms: building design, climate control, feeding systems, etc.
Biocheck.UGent is an independent, risk-based, scientific scoring system for assessing the quality of your on-farm biosecurity.
Environmental Footprint Calculator along the pork value chain.
Definition for the most commonly used pig terms
Simulator that calculates the amount of drug to add to the water when using a flow dispenser.
Use this tool to explore which slurry management strategy best fits your situation. Click on the flow chart or on the buttons within the text to navigate through the different parts of the tool.
Weekly newsletter with all the pig333.com updates
List of the most important diseases and conditions in pigs. Symptoms, causes, diagnosis, control and prevention of each disease are described. Some of the treatments mentioned may be prohibited in some countries. Information on all diseases to be completed in the coming days.
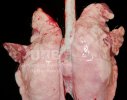
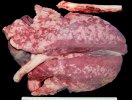
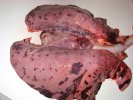
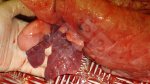
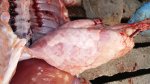
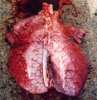
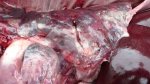
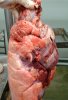
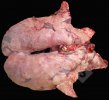
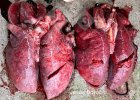
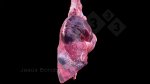
Influenza is a respiratory disease of high importance due to its fast transmission and zoonotic potential.
Porcine influenza is caused by several Influenza Type A viruses closely related, characterized to have the ability to change the antigenic structure and create new strains.
Each serotype is identified through surface proteins called "H" and "N". The three most common serotypes affecting pigs are H1 N1, H1 N2 and H3 N2. There are also different strains of these serotypes that have different pathogenicity and no crossed protection.
The incubation period is very short, 12 to 48 hours. It affects the respiratory system. The virus can infect a farm in few days. This high transmission is almost the main feature helping in the diagnosis.
There are three important periods in which the disease can cause infertility, and all of them are caused by fever and its consequences depending on the pregnancy stage because the virus is not systemic and does not cross the placenta. Thus, fetuses are not infected.
In big farms, influenza can end up being endemic with intermittent outbreaks of clinical symptoms and infertility. Different strains can consecutively affect one farm.
Sows
When the virus enters a farm for the first time, 2 or 3 animals show symptoms of disease during the first 2 days, followed by:
In the rest of the farm:
Lactating piglets
Weaners and growers
Acute Disease
Endemic Disease
Influenza can be introduced by:
In the acute disease, a reliable diagnosis can be done based on clinical signs, due to the fact that there are no other diseases with such a dramatically quick transmission and clinical effects. Blood samples taken from sows at the beginning of the disease and 2 to 3 weeks after, show an increase in antibody titters. Influenza virus can be identified from nasal swabs analyzed by PCR. Oral fluids can also be used, with good results.
However, the endemic disease can be difficult to differentiate form other viral diseases. PRRS and Aujeszky’s disease must be considered.
Sequencing is critical to establish the vaccine strain.

What laboratory diagnostic methods can I use to diagnose influenza A? Which one should I choose according to the situation? How do I interpret the results?

In this last article of the series, we discuss management strategies and the vaccines available to control swine influenza.

The clinical picture associated with swine influenza is often complicated by temperature fluctuations, other viruses, or bacteria. In part two of this series, we look at the clinical signs of this disease.