Coccidiosis
The Coccidiosis disease is caused by intracellular protozoan parasites causing mainly diarrhea in piglets.
Alternative names: Isospora suis, Cryptosporidium
Information
Coccidiosis is caused by small parasites that multiply inside the host cells, mainly from the digestive tract. There are three types: Eimeria, Isospora and Cryptosporidium.
Isospora suis is the most pathogenic of the three coccidia species.
The disease is frequent and is widely spread in piglets, although it can occasionally be seen in growing and finishing pigs, as well as in boars, at the time they are transported or when housed in infected barns that are continuously used.
We must suspect of coccidiosis if there is diarrhea in piglets from days 7 to 21 of age that do not respond very well to antibiotics.
Symptoms
Sows
- No symptoms present. They are carriers.
Lactating piglets
- In the early stages, diarrhea is the main symptom.
- In late stages, feces can have different consistency and color, which can vary from yellow to grey or green, or can have blood, depending on the severity of the disease.
- Dehydration is common.
Weaners and growers
- Slow growth
- Loose feces.
- Feces can sometimes be bloody.
Causes / Contributing Factors
- Dirty pens.
- Poor cleaning of farrowing crates
- Damaged and humid flooring.
- Hot and humid weather.
- Floor feeding of piglets.
- Flies.
- Dry feces behind gestation crates.
- Barns used in a continuous flow without cleaning and disinfection.
Diagnosis
It is better to take feces samples from pigs in the recovery process than from animals presenting diarrhea for its analysis. The diagnoses is easier if a live pig is sent to the lab in order to perform histological analysis of the intestinal wall.
Control/Prevention
- In order for the treatment to be effective, it must be administered before the intestinal wall is colonized.
- The effectiveness of the different treatments depends on the kind of coccidia affecting the animal.
- Medicate the sows feed with amprolium premix, monensin sodium or sulfadimidine. These antibiotics must be administered when the sows enters the farrowing area and through all the lactation.
- Inject each litter with long lasting sulphonamide at 6 days of age.
- Medicate small amounts of milk powder with an anti coccidiate like amprolium or salinomicin, and administer small amounts daily to the piglets from 3 days of age on.
- One dosage of 6.25 mg/kg of toltrazuril controls the disease effectively.
- Depopulate and clean all the barns using disinfectants to kill the oocysts of the coccidia.
- In adult animals the disease disappears on its own.
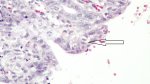
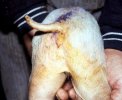
Atlas of pathology
See images in the Altlas related to Coccidiosis