Technical UPDATE | Tonisity Px for Sows Reduces Antimicrobial Consumption
Key Takeaways
Two studies assessed the impacts of Tonisity Px supplementation of weaned pigs or sows and their litters on antimicrobial usage and growth performance during major transition/developmental periods.
>Piglets that received Tonisity Px during a 6-day peri-weaning period required 34% fewer medical treatments in the nursery and improved 6-week post-weaning growth rate 3.9%.
>Supplementation of sows with Tonisity Px for 7 days pre-farrowing and preweaning reduced antibiotic treatment needs of piglets 63% and improved their growth rate (ADG +16%, weaning weights +400g/pig).
>Tonisity Px offers a non-antibiotic option to help pigs transition through production milestones, resulting in less antibiotic usage, costs, and labor associated with treatment administrations.
Swine producers must confront a host of health and productivity challenges as they continually seek profitably under uncertain circumstances. Even long-used tools such as oral and/or injectable antimicrobials are now under scrutiny by today’s markets and consumers. Furthermore, regulatory and industry efforts in recent years have sought to limit antimicrobial usage by requiring veterinary supervision for many products while actively advocating for ‘judicious use’ principles. Because of these relatively recent changes in industry practices and priorities, many swine producers and veterinarians are searching for strategic, non-antibiotic alternatives that can help them continue to farrow sows, nurse and wean piglets, and stock nurseries with animals that are healthy, productive, and profitable.
Tonisity Px™
Tonisity Px is a highly palatable, readily consumed, isotonic solution of amino acids and electrolytes that provides microenteral nutrition to intestinal cells. It is the first isotonic protein drink for pigs. Developed exclusively for swine, it is a cost-effective break-through technology. Tonisity Px is NOT just another electrolyte solution of salt and sugar, or another yeast/probiotic/ enzyme feed additive. Rather, it is strategically formulated to provide the right combination of key amino acids and micronutrients that encourages the development of a high-functioning intestinal system (especially the duodenum) and helps hydrate the animal. Specifically, Tonisity Px nourishes enterocytes and has been shown to increase villi height (taller villi absorb more nutrients and fluids). Improved gut function thereby helps boost herd health and productivity.
Tonisity Px is a powder designed for mixing with water to create a 3% solution. Small amounts can then be offered (in a pan or mixed with feed) to neonatal and/or weaning-age pigs, gestating sows, or pigs of any age or class whenever stress or production milestones might typically pose health or performance set-backs. Two studies were recently conducted to evaluate the impact of Tonisity Px supplementation of weaned pigs or sows and their litters on antimicrobial usage and growth performance during major transition/developmental periods (e.g., lactation, post-weaning nursery).
Weaned Pigs Study
Experiment Design
A research study investigated the effects of Tonisity Px supplementation at weaning on subsequent morbidity, antibiotic usage, and growth of pigs during the immediate 6 weeks post-weaning.
The study involved 178 pregnant sows and gilts housed at a large, 5000-head commercial US sow farm with a stable health status. Sows/gilts were blocked by parity and randomly assigned to 2 treatment groups (Tonisity Px n=88, controls n=90), designations that would apply to their eventual litters. At farrowing, piglets were individually weighed and scheduled for weaning at 20 days of age. Litters assigned to the Tonisity Px group received the following supplementation schedule:
- At 2 to 8 days of age, and at 3 and 2 days pre-weaning, litters were offered 500 mL/day of Tonisity Px 3% solution;
- 1 day before weaning, litters were offered 1 kg of Tonisity Px gruel mixture;
- At weaning (moved to nursery) and for 2 more days, pigs were offered 100 g/pig of gruel mixture twice daily.
Control litters did not receive any supplementation. All pre-weaning Tonisity Px administrations were placed in a metal creep feeder. The gruel mixture was made with 3% Tonisity Px solution combined with dry, bagged creep feed (mixed into an ‘oatmeal’ consistency). Post-weaning gruel was prepared using 3% Tonisity Px solution on the day of weaning, 1.5% solution for day 1 post-weaning, and 0.75% for day 2 post-weaning. Consumption of the solution and gruel was monitored and any residual quantities recorded. Upon arrival in the nursery, 1885 weaned pigs (n=949 control; n=936 Tonisity Px) were placed by treatment group into 38 pens (blocked by weight, gender, and location; ~50 pigs/pen). Pigs with critical health status at the time of placement (e.g., recumbent, unable to walk, chronically lame) were removed from the study. All pens were provided feed and water according to standard practices, and pen feed consumption was automatically recorded. Individual body weights (BW) were obtained on the day of weaning and again at 6-weeks post-weaning.
Pigs were monitored daily for any evidence of disease or mortality, and scored for scours status twice weekly. Antimicrobial treatments/medications were administered as needed following veterinary direction (not controlled by study protocol). Collected data regarding treatments, BW, and average daily gain (ADG) were statistically analyzed by appropriate standard methods using the pig as the experimental unit. Significance between treatments was declared at P ≤ 0.05.
Results
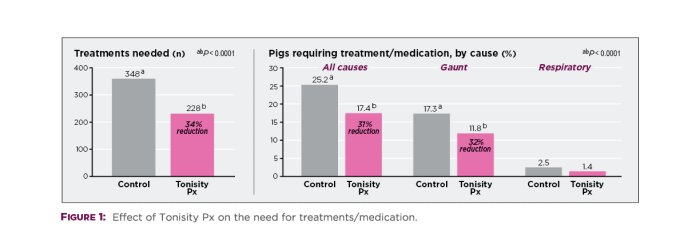
Pigs supplemented with Tonisity Px shortly before and after weaning experienced large reductions in their needs for antimicrobial treatments and medications during the subsequent 6 weeks in the nursery. Results summarized in Figure 1 indicate that 34% fewer treatments were required by pigs in the Tonisity Px group compared to controls (P < 0.0001). The percent of pigs needing medication significantly fell by 31% for all causes of illness (P < 0.0001) and by 32% for pigs specifically medicated for being gaunt (P < 0.0001). Even rates of pigs treated for respiratory signs trended lower in the Tonisity Px group (P = 0.075).
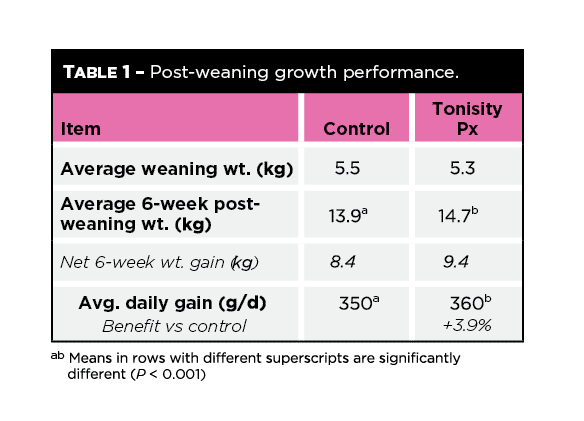
Pigs supplemented with Tonisity Px also demonstrated significantly (P < 0.001) heavier BW than controls by 6 weeks after weaning (Table 1), and averaged 0.8 kg (5.9%) more net weight gain/head. Thus, post-weaning ADG improved 3.9% (P < 0.001) during the 6-week post-supplementation period.
Sow Study
Experiment Design
A second study investigated the effects of Tonisity Px supplementation of sows before farrowing and again before weaning on subsequent piglet morbidity, antibiotic usage, and growth until weaning.
The study was conducted in the summer at a commercial production facility that had experienced a PRRS outbreak the previous month and had chronic issues with neonatal rotavirus diarrhea. A total of 103 sows (Landrace × Large White × Tai Zumu) were enrolled in the study and randomized to 1 of 3 treatment groups:
- Control (no supplementation);
- Tonisity Px 120: sows offered 120 mL of 3% Tonisity Px solution daily for 7 days pre-farrowing and 7 days pre-weaning;
- Tonisity Px 500: sows offered 500 mL of 3% Tonisity Px solution daily for 7 days pre-farrowing and 7 days pre-weaning.
Sows were fed standard rations 3 times daily (normal farm procedure), and Tonisity Px solution was top-dressed on the second daily feeding.
Sows farrowed 1208 piglets that were weighed within 24 hours of birth (n=415 controls; n=406 Tonisity Px 120; n=387 Tonisity Px 500). All piglets, regardless of sow treatment group, were offered Tonisity Px (500 mL/litter in an open pan) once daily from days 2 to 8 of age, and creep feed was provided to all litters beginning at 10 days of age.
Piglets were weaned at approximately 21 days of age and weighed. Individual antibiotic injections administered to either sows or piglets were recorded daily. Antimicrobial treatments (i.e., a combined injection of gentamicin and amoxicillin) were administered as needed for neonatal diarrhea by barn staff according to farm standard operating procedures and were not controlled by study protocol.
Collected data regarding treatments, weaning BW, and weaning ADG were statistically analyzed by appropriate standard methods using litter as the experimental unit. Significance between treatments was declared at P ≤ 0.05. Odds ratios were also calculated for antibiotic usage in piglets.
Results
Piglets from sows supplemented with Tonisity Px for 7 days before farrowing and weaning demonstrated substantial reductions in their need for antimicrobial treatments and medications during lactation, even though the study was conducted under challenging health and environmental conditions.
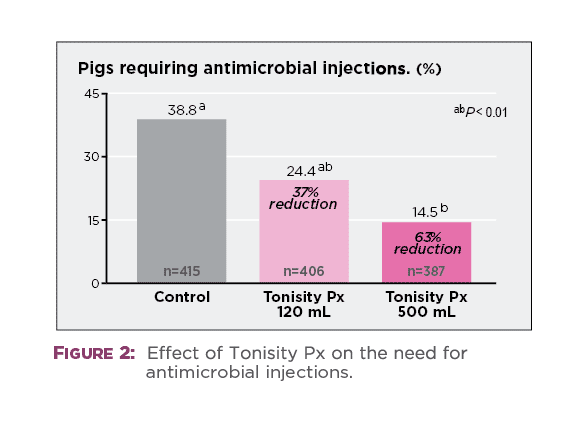
Results summarized in Figure 2 reveal that 500 mL/day of supplementation with Tonisity Px helped reduce the need for antimicrobial treatment by 63% compared to controls (P < 0.01). While the 37% reduction in the 120-mL Tonisity Px group was also notable, significance from controls was not achieved (P > 0.05). Calculation of odds ratios for the likelihood of antibiotic injections in each treatment group provided further insight. Control piglets were 3.75-times (P < 0.01) more likely to receive an antibiotic injection compared to piglets in the Tonisity Px 500 mL/day group, and 1.97-times (P < 0.01) more likely than piglets in the 120 mL/day group.
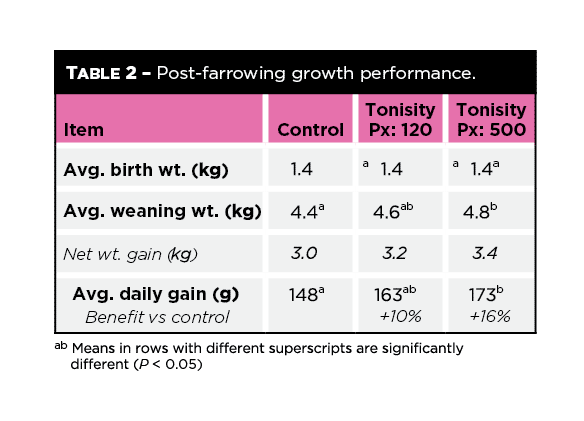
In addition to morbidity reductions in the 500-mL Tonisity Px group, improved rates of growth were also observed (Table 2). Piglets from sows supplemented with 500 mL of Tonisity Px generated significant (P < 0.05) improvements in both weaning weight (9%, +400 g) and ADG (16%), while the 120-mL dose rate of Tonisity Px provided numerical improvements but did not achieve significance (P > 0.05).
A linear dose response to Tonisity Px was clearly evident in this study for both antimicrobial usage and weight gains of piglets. The largest benefits were observed for sows receiving 500 mL/day of Tonisity Px vs controls, while responses were intermediate for sows receiving just 120 mL/day.
Conclusions
In 2 studies, supplementation of piglets or sows with Tonisity Px prompted reductions in antibiotic usage and gains in productivity that were both statistically and practically significant. Tonisity Px supplementation during a 6-day peri-weaning period helped nursery pigs reduce their need for medical treatments by 34% and improved post-weaning growth rate 3.9%. Similarly, supplementing sows with 500 mL/day of Tonisity Px for 7 days pre-farrowing and pre-weaning helped piglets reduce antibiotic treatment needs 63% while boosting ADG 16% and elevating weaning weights by 400 g/pig. These consistent benefits of Tonisity Px across both studies were likely due to several factors, such as improved hydration and ingestion of gut-supportive micronutrients and proteins.
The economic and veterinary benefits of using Tonisity Px to help reduce antimicrobial usage are highly relevant for contemporary swine production and consumer markets. Tonisity Px supplementation of sows and/or piglets presents a nonantibiotic option to help animals transition through farrowing, lacatation, and weaning, resulting in reductions in antibiotic usage, antibiotic costs, and labor associated with treatment administrations. Furthermore, these outcomes offer a rare and substantial opportunity to not only markedly reduce input costs associated with health issues but also boost productivity.
References
1. Firth AM, Cano GL, Alujas AM. Effect of Tonisity PxTM administration on intestinal morphology. Am Assoc Swine Vet 2017; poster presentation.
2. Data on file, Study Report T42, Tonisity Int. Ltd.
3. Data on file, Study Report 17-003, Tonisity Int. Ltd.
Tonisity Px is an isotonic nutritional supplement designed specifically for pigs. It is not a drug and it does not contain ingredients with drug-like properties. It is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Any observed differences in performance are due to the nutritional and hydration properties of Tonisity Px.
16 Fitzwilliam Place, Dublin 2, Ireland
Tel +353 1 902 0026 www.tonisity.com
Tonisity Px™ is a trademark of Tonisity Int. Ltd. ©2018
Tonisity International Ltd.
Welcome to 333
Connect, share, and interact with the largest community of professionals in the swine industry.
Celebrating 138270Users on 333!
Sign upAlready a member?