An update on macrolide antibiotics in pig production

Porcine respiratory disease poses a significant challenge to pig producers due to its impact on production efficiency and animal welfare
- Antibiotics play a crucial role in reducing the impact of disease.
- Tylvalosin, a macrolide antibiotic, has additional immunomodulatory benefits.
- When used judiciously, tylvalosin is a cost-effective solution that aligns with the principles of antibiotic stewardship.
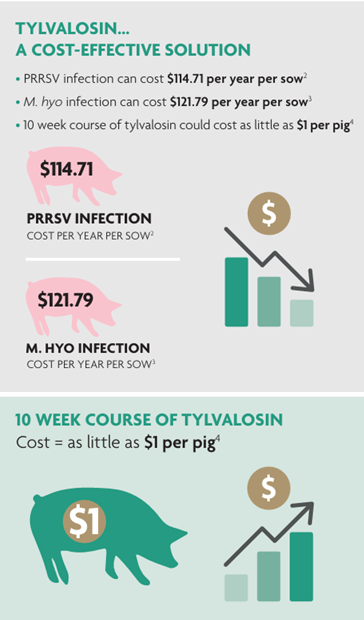
Tylvalosin is a cost-effective solution
 The use of macrolide antibiotics, such as tylvalosin, has been shown to be beneficial both in terms of treatment of disease, control, and prevention of the spread of infection and improvement in production efficiencies and economic outcomes. A recent study looked at the effects of oral tylvalosin on disease caused by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) alone in sows, or in combination with Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (M. hyo) in piglets.
The use of macrolide antibiotics, such as tylvalosin, has been shown to be beneficial both in terms of treatment of disease, control, and prevention of the spread of infection and improvement in production efficiencies and economic outcomes. A recent study looked at the effects of oral tylvalosin on disease caused by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) alone in sows, or in combination with Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (M. hyo) in piglets.
Understanding Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae
- Primary causative agent in Enzootic Pneumonia (EP)
- Signs include coughing, fever, pneumonia, and increased susceptibility to other respiratory infections
- Secondary bacterial infection often results in more severe disease
- Affects pigs worldwide
- Leads to reduced growth rate and poorer production efficiency
Understanding porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS)
- Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) is globally endemic.
- Causes significant welfare issues for affected animals.
- Loss of condition, inappetence and pneumonia in piglets.
- Reproductive failure in sows with an increase in stillbirths, abortions, and fetal mummifications.
- Increase in piglet mortality from infected sows.
- Major cause of economic loss.
Unlocking the power: tylvalosin’s immunomodulatory advantage
M. hyo and porcine reproductive and respiratory disease virus are components of the Porcine Respiratory Disease Complex (PRDC). In many cases, a combination of respiratory pathogens causes much more severe disease than a single pathogen.
Cases of porcine respiratory disease are often treated with antibiotics. Tylvalosin not only demonstrates efficacy against respiratory pathogens including M. hyo, but also exhibits additional immunomodulatory benefits. It is suggested that these immunomodulatory effects may be responsible for tylvalosin’s beneficial effects against pathogens like PRRSV.
 Immunomodulatory benefits
Immunomodulatory benefits
Tylvalosin exhibits additional immunomodulatory benefits
The on-farm use of tylvalosin: a 2023 study1
- The effect of a water-soluble formulation of tylvalosin (Aivlosin® 625mg/g granules) on disease caused by PRRSV and M. hyo was investigated in piglets and breeding sows.
- Tylvalosin reduced M. hyo counts in the lungs.
- Tylvalosin showed a highly significant immunomodulatory effect on multiple cytokines in sows and piglets challenged with M. hyo and / or PRRSV.
- Tylvalosin may reduce PRRSV shedding in piglets following transplacental infection in sows.
These findings indicate that the responsible use of tylvalosin in operations with coexisting M. hyo and PRRSV infections will have a measurable impact on animal health.
Porcine respiratory disease and the on-farm impact of tylvalosin
- Better disease management.
- Improved animal welfare.
- Improved profitability.
Antibiotic stewardship and tylvalosin
The commitment to safeguarding animal welfare includes the use of antibiotics prescribed by a veterinarian after diagnosis both to reduce the incidence of disease and suffering, and to support pig producers and veterinarians in the production of safe food from healthy animals (NOAH, 2016).
Antibiotic stewardship is needed to reduce the growing problem of antibiotic resistance
However, antibiotics play a crucial role in both human and animal health. Responsible prescribing of antibiotics, or so-called antibiotic stewardship, is needed to reduce the growing problem of antibiotic resistance, and the consequent One Health implications.
Antibiotics should only be prescribed to animals under veterinary care and after diagnostic confirmation with appropriate laboratory testing. Tylvalosin aligns with the principles of antibiotic stewardship:
- Tylvalosin has a low effective therapeutic dose and short withdrawal period.
- Tylvalosin has proven efficacy against respiratory pathogens, including M. hyo.
 Targets infection
Targets infection
Tylvalosin has proven efficacy against respiratory pathogens, including M. hyo.
References
- Rodriguez A.L., et al. Effects of a water-soluble formulation of tylvalosin on disease caused by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus alone in sows or in combination with Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae in piglets. BMC Vet Res. 2023 Feb 1;19(1):31
- Holtkamp D.J., et al. Assessment of the economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus on United States pork producers J. Swine Health Prod. 2013. 21(2):72-84.
- Yeske, P. 2016. Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae elimination, 2016 AASV Annual Meeting Proceedings, pg. 376-380. https://www.aasv.org/library/swineinfo/item.
- Jansen T, et al. Assessing the Value of Antibiotics on Farms: Modeling the Impact of Antibiotics and Vaccines for Managing Lawsonia intracellularis in Hog Producers. Front Vet Sci. 2019 Oct 18;6:364
Contact:
Contact us using the following form.

